Projekty
Automating the testing of athletes for muscle fatigue asymmetry
Opublikowano: 2 listopad 2023
Wykonawcy projektu: Jędrzej Ślachciak, Aleksandra Grohs
In this study, we would like to present the results of the process of developing a research method for analyzing the performance of athletes’ muscles, and more specifically, their asymmetry of fatigue[1,2]. The purpose of our system is to learn about the stronger and weaker aspects of the musculoskeletal apparatus in a group of athletes of different sports, and more specifically to detect the muscular imbalance of individual muscle parts. In addition, it was assumed to use the results of the study to draw up an individualized training plan supported by the current level of training. An example of such conduct is presented in the article [3]. Another goal was to determine the fatigue thresholds of individual muscle groups. The project is mainly focused on the musculature of the lower extremities and lower torso.
During the study, the greatest attention has been given to the areas of the following muscles: quadriceps of the thigh, biceps of the thigh, gastrocnemius, and rectus abdominis muscle. To measure the signals, an EMG system was used – the Noraxon TeleMyo 2400 G2 measuring the voltage produced by the muscle belly [4]. It consisted of eight reference electrodes collecting noise signals from the skin surface and 16 electrodes measuring electric potential generated by muscle as well as a receiving station connected to a computer. Exercises could be modified according to the subject’s needs, but the basic one were squats with a load of ten kilograms, performed in five series for twenty seconds.
The pure signal from the survey is not enough, and in order to read meaningful data from it, it must be processed properly [5]. In order to automate this process, an algorithm was created in Python language. The aim of the program is to automaticially generate numericial data and their graphical representations. Examples of the parameters were:
the average value in the time intervals in each series,
the average value in the series,
the Fourier transform of the signal,
the maximum percentage value in the series,
the integral determined from a graph of the voltage waveform over time.
A diagram of the whole procedure can be seen in Figure 1.
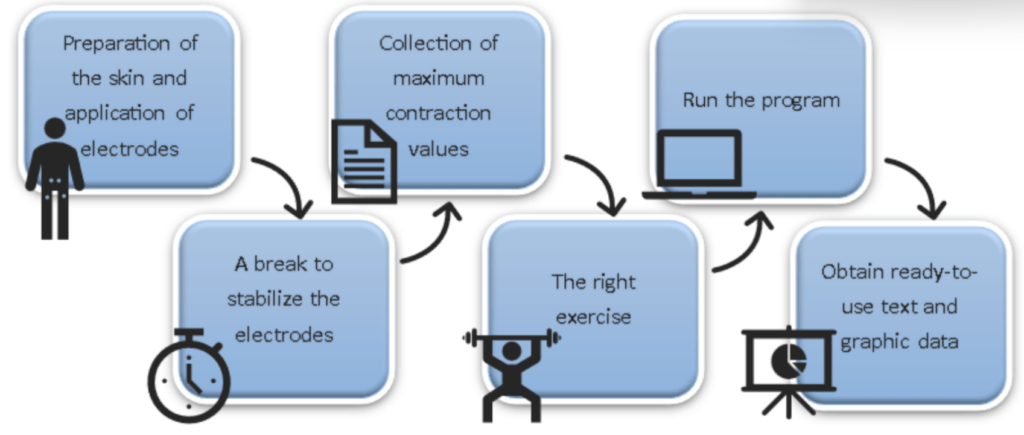
Fig. 1. Diagram of the procedure
The program was tested on four sets of data from individuals in the 20-25 age range. As a result, five parameters each representing the activity of a particular muscle group were successfully obtained. All subjects experienced some asymmetries, which in 75% of the subjects increased slightly over time. In one person, the increase in asymmetries was particularly large, due to a past injury.
Thanks to the high speed of data processing enabled by the system, it can find application in physiotherapy offices as a control of applied therapies or training. The resulting compensation of muscular asymmetries can significantly contribute to increased athletes’ performance. The developed method would also significantly facilitate the work of physicians by giving easy-to-read and easy to compare data that can suggest sources of injury and pain.
References:
[1] Y. Zheng et al., Effect of core stability training monitored by rehabilitative ultrasound image and surface electromyogram in local core muscles of healthy people., Pain Research and Management, 2019, 2019, 1-8.
[2] J.J.B. Allen et al., Manipulation of frontal EEG asymmetry through biofeedback alters self‐reported emotional responses and facial EMG., Psychophysiology, 38, 2001, pp. 685-693.
[3] Y. Dai et al., MSEva: A musculoskeletal rehabilitation evaluation system based on EMG signals., ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 19, 2022, 1-23.
[4] B. Farnsworth, What Is EMG (Electromyography) and How Does It Work?, 2018, https://imotions.com/blog/learning/research-fundamentals/electromyography-101/, access: 20.06.2023.
[5] P. Konrad, The abc of emg. A practical introduction to kinesiological electromyography., Noraxon Inc. USA, Scottsdale, 2006.
